NEET
What Is NEET?
NEET (UG), formerly the All India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT), is an all India pre-medical entrance test for students who wish to pursue undergraduate medical (MBBS), dental (BDS), and AYUSH (BAMS, BUMS, BHMS, etc.) courses in government and private institutions in India and also, for those intending to pursue primary medical qualification abroad
NEET is been conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA) has been established as a premier, specialist, autonomous, and self-sustained testing organization to conduct entrance examinations for admission/fellowship in higher educational institutions. Around 600 colleges take admission through NEET for approximately 40000 seats

What we do
Important Points
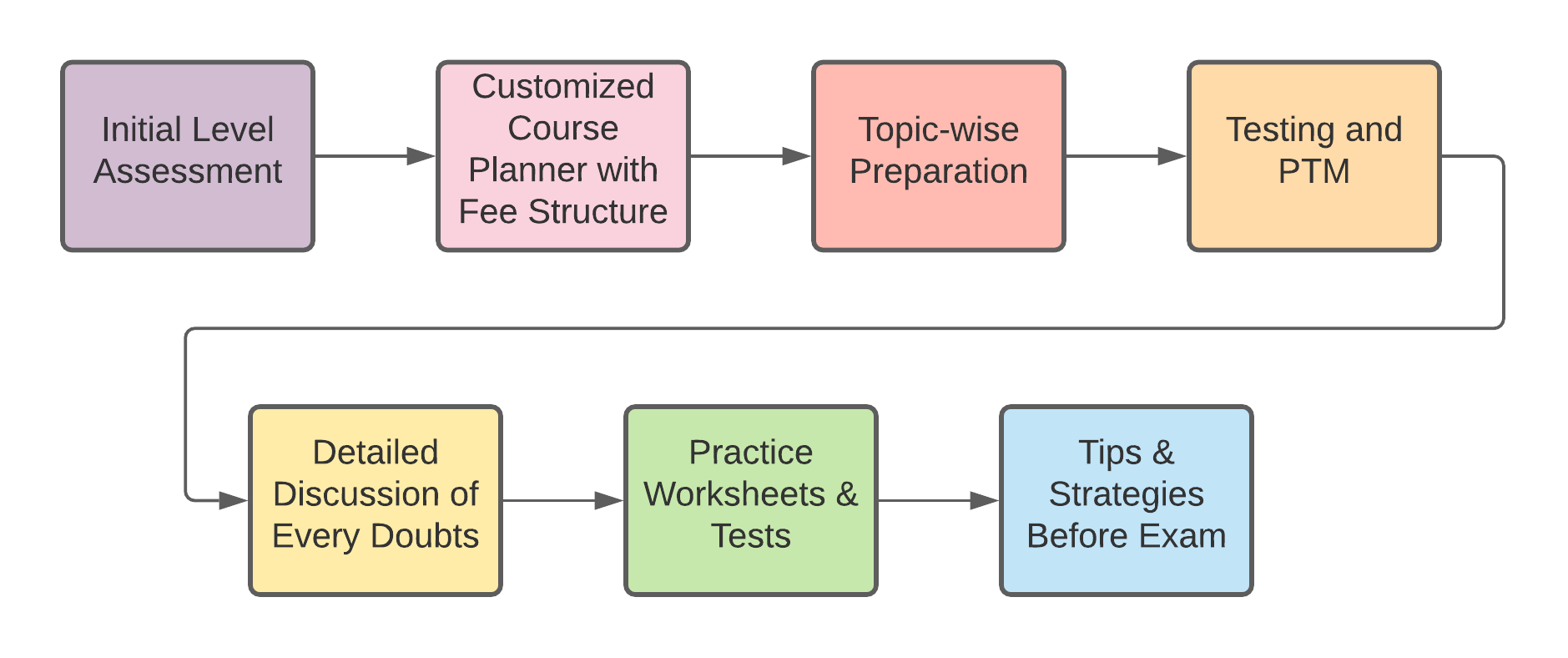
Method Of Preparation
NEET
1. Diversity of Living Organisms
2. Structural Organisation in Plants & Animals
3. Cell: Structure and Function
4. Plant Physiology
5. Human Physiology
6. Reproduction
7. Genetics and Evolution
8. Biology and Human Welfare
9. Biotechnology and its Applications
10. Ecology and Environment
1. Physical-world and measurement 11. Electrostatics
2. Kinematics 12. Current Electricity
3. Laws of Motion 13. Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism
4. Work, Energy and Power 14. Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current
5. Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body 15. Electromagnetic Waves
6. Gravitation 16. Optics
7. Properties of Bulk Matter 17. Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
8. Thermodynamics 18. Atoms & Nuclei
9. Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory 19. Electronic Devices
10. Oscillation & Waves
1. Basic Concepts of Chemistry
2. Structure of Atom
3. Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties
4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
5. States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
6. Thermodynamics
7. Equilibrium
8. Redox Reactions
9. Hydrogen
10. s-Block Elements
11. Some p-Block Elements
12. Organic Chemistry
13. Solid States
14. Solutions
15. Electrochemistry
16. Chemical Kinetics
17. Surface Chemistry
18. Isolation of Elements
19. p-block elements
20. d- and f-Block Elements
21. Coordination Compounds
22. Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
23. Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
24. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids